Discover the Critical Role of Hydration in Maximising Health and Performance
Grasping the Crucial Importance of Hydration During Hot Weather
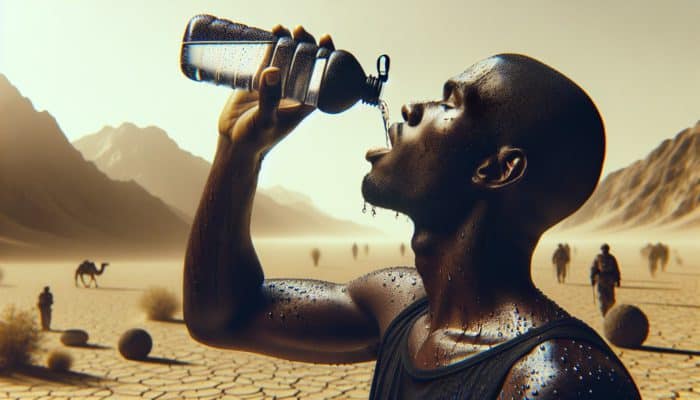

In scorching climates, prioritising hydration is essential for sustaining critical bodily functions, preventing serious heat-related illnesses, and promoting overall health and well-being. The significance of water extends beyond quenching thirst, playing a pivotal role in various physiological processes, including temperature regulation, nutrient transport, and waste elimination. As the external temperature soars, the body experiences rapid fluid loss, making it imperative to prioritise hydration to counteract these detrimental health effects.
The primary advantages of maintaining proper hydration during hot weather encompass:
- Enhanced physical performance: Staying adequately hydrated is vital for achieving optimal muscle performance and endurance, leading to improved athletic outcomes.
- Effective temperature regulation: Water is indispensable for sustaining a stable body temperature, preventing overheating and associated health hazards.
- Improved cognitive function: Sufficient hydration is crucial for maintaining focus, concentration, and mental clarity, all essential for productivity and effective decision-making.
- Lowered risk of heat-related illnesses: Adequate hydration drastically reduces the chances of experiencing critical conditions like heat exhaustion and heatstroke, which can be life-threatening.
Recognising these benefits can motivate individuals to make hydration a priority, especially when engaging in outdoor activities or facing prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures.
Recognising the Harmful Effects of Dehydration
Dehydration can lead to severe health issues, particularly in hot environments where the risk of heat-related illnesses significantly escalates. When the body loses more fluids than it takes in, it struggles to function optimally, causing complications such as heat exhaustion and heatstroke. Symptoms can initially appear subtle but may rapidly escalate if not promptly addressed.
Key indicators of dehydration include:
- Dizziness: An early warning sign indicating that the body lacks sufficient fluids to operate effectively.
- Fatigue: Decreased energy levels can both stem from and contribute to dehydration, creating a vicious cycle that exacerbates the situation.
- Dry mouth: A clear signal from the body that it requires more fluids to function correctly.
- Decreased urine output: Dark yellow urine suggests concentrated waste products, highlighting inadequate hydration levels.
Identifying these early symptoms is vital for circumventing severe health complications. In extreme cases, dehydration can result in confusion, seizures, or even loss of consciousness, underscoring the necessity of proactive hydration efforts.
Daily Water Intake Guidelines for Maintaining Optimal Health
General recommendations advocate for the consumption of at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water daily, equating to approximately 2 litres or half a gallon. However, in hot climates, this baseline may require substantial adjustments based on individual needs, levels of physical activity, and environmental conditions.
For individuals engaging in vigorous physical activities or spending extended periods outdoors, daily water intake should be significantly increased. Common guidelines suggest:
- 1.5 to 2 litres for light activities in moderate heat.
- 2 to 3 litres during intense workouts or in extreme heat conditions.
- Additional fluid intake is crucial for individuals with higher body mass or those who experience excessive sweating.
- Individual considerations: Factors such as age, gender, and overall health can greatly influence hydration requirements.
Monitoring thirst levels and observing urine colour can provide additional insights into hydration status, ensuring individuals remain healthy and functional even under challenging conditions.
Proven Strategies for Sustaining Hydration in Hot Weather

Effective Practices for Optimising Hydration
Experts recommend implementing various best practices to maximise hydration during hot weather. Drinking water consistently throughout the day is essential since relying solely on thirst cues can lead to inadequate hydration, especially in extreme temperatures.
To ensure effective hydration, consider adopting the following actionable strategies:
- Establish a hydration routine: Kick off your day with a glass of water and set reminders to drink throughout the day, promoting consistent fluid intake.
- Limit excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption: Both substances function as diuretics, potentially leading to decreased water levels in the body.
- Incorporate hydrating foods: Include fruits and vegetables such as watermelon, cucumbers, and oranges that contribute to your overall fluid intake while delivering essential nutrients.
- Adjust fluid intake based on conditions: Increase your water consumption during physical activities or exposure to high temperatures, aiming for small sips frequently to avoid overwhelming your system.
By integrating these practices into daily life, individuals can effectively maintain hydration, supporting their health and well-being in hot weather conditions.
How to Spot Early Symptoms of Dehydration
Recognising the early signs of dehydration is crucial for preventing more severe health issues. Symptoms such as thirst, dry mouth, and dark urine serve as initial indicators that water intake is insufficient. These signs can be subtle and easily overlooked, making it essential to take a proactive approach to hydration.
For example, a hiker on a trail may not immediately notice dehydration until they begin to feel dizzy or fatigued. However, taking frequent sips of water can help maintain hydration levels before these symptoms become pronounced. Real-life examples include:
- Office workers frequently neglect to drink water throughout the day; setting reminders can assist in improving their hydration habits.
- Outdoor athletes should diligently monitor their fluid intake during extended events to avoid sudden fatigue and performance declines.
- Children playing outside may not feel thirsty, so caregivers must encourage regular hydration breaks to ensure they remain hydrated.
- Travellers in hot climates should prioritise hydration, as unfamiliar environments can lead to underestimating their fluid needs.
Recognising these early symptoms empowers individuals to take timely action, ultimately ensuring their health and safety in hot conditions.
The Essential Role of Electrolytes in Effective Hydration

Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium, are crucial for hydration as they help regulate fluid balance within the body. These vital minerals facilitate various physiological functions, including nerve signalling and muscle contractions. When the body loses fluids through sweating, it also loses essential electrolytes, making it imperative to replenish both to sustain optimal health.
Sports drinks can be advantageous for individuals engaging in prolonged physical activities in hot climates, as these beverages typically contain a well-balanced mix of electrolytes and carbohydrates. However, not everyone requires these drinks. Key considerations include:
- Activity intensity: Moderate exercisers may not need sports drinks, while athletes participating in endurance events likely do.
- Duration of exercise: Workouts lasting over an hour in the heat typically necessitate electrolyte replenishment to maintain performance.
- Individual sweat rates: Those who sweat excessively may require additional electrolytes to maintain balance and prevent cramping.
- Dietary sources: Consuming foods rich in electrolytes, such as bananas for potassium or nuts for magnesium, can effectively support hydration.
Understanding the importance of electrolytes and recognising when to supplement them can significantly enhance hydration strategies, ensuring optimal performance and health in hot climates.
Calculating Water Intake Requirements in Hot Weather
Experts generally recommend that individuals in hot climates aim for at least 8 to 10 glasses of water daily. However, this guideline should be modified based on specific circumstances, including activity level, sweat loss, and individual health considerations.
For various age groups, the required amount of water can differ significantly:
- Children: Require regular hydration breaks to compensate for their higher metabolic rates and smaller body sizes, which increases their vulnerability to dehydration.
- Adults: Should target the baseline of 8 to 10 cups, increasing intake during exercise and in extreme weather conditions to maintain hydration.
- Elderly individuals: Need reminders to drink, as their thirst response may diminish with age, making them more susceptible to dehydration.
- Athletes should develop tailored hydration strategies that account for sweat loss, often exceeding 3 litres during intensive training sessions.
Monitoring hydration status through urine colour and adjusting intake based on environmental conditions can help ensure that individuals effectively meet their hydration needs.
Evaluating the Necessity of Sports Drinks During Physical Activity
Sports drinks can be beneficial for certain populations, particularly athletes and individuals participating in prolonged physical activities in hot conditions. These beverages aid in replenishing lost electrolytes and providing rapid energy through carbohydrates. However, sports drinks are not universally essential for all individuals.
Consider the following factors when determining their use:
- Activity level: Casual exercisers or those engaged in light activities may find plain water sufficient without the added sugars or calories from sports drinks.
- Exercise duration: Activities lasting less than an hour typically do not require electrolyte replenishment, making water a suitable choice.
- Personal health considerations: Individuals with specific health conditions should consult health professionals regarding the consumption of sports drinks, as they may have unique hydration needs.
- Hydration goals: Those aiming to maintain a healthy weight or limit sugar intake might prefer plain water over sugary sports drinks to support their overall health.
Ultimately, understanding personal hydration needs and activity requirements is crucial in determining whether sports drinks are warranted, ensuring effective hydration and overall well-being.
The Influence of Hydration on Physical Activity and Athletic Performance
How Proper Hydration Enhances Athletic Performance
Sufficient hydration is fundamental for optimal physical performance, as it significantly influences how the body functions during exercise. Proper fluid intake aids in regulating body temperature, maintaining cardiovascular stability, and supporting muscle function. Conversely, even mild dehydration can lead to diminished endurance, strength, and overall athletic performance, impacting training and competition effectiveness.
Research indicates that just a 2% loss of body weight due to dehydration can impair physical performance in various ways:
- Reduced endurance: Dehydrated individuals may experience quicker fatigue during exercise, limiting their ability to sustain activity levels.
- Increased perceived effort: Tasks that typically feel moderate can become significantly more challenging when dehydration sets in, affecting performance and motivation.
- Slower reaction times: Dehydration can impair cognitive function, leading to slower decision-making during athletic events, which can prove detrimental.
- Heightened risk of injury: Muscle cramps and joint discomfort are more likely to occur when dehydration impacts the body, increasing injury risks.
By prioritising hydration, athletes can enhance their performance, reduce the risk of injury, and ultimately achieve their fitness objectives, particularly in challenging heat conditions.
Best Practices for Hydration Before and After Exercise
Drinking water before and after exercise is critical for maintaining hydration levels, especially in hot climates. Pre-hydration prepares the body for physical exertion, while post-exercise hydration aids recovery and fluid balance restoration.
For effective pre-hydration, individuals should aim to:
- Consume 16-20 ounces of water approximately two hours before exercising to ensure adequate fluid levels.
- Drink an additional 8-10 ounces just before commencing physical activity for optimal hydration.
- Monitor hydration levels by observing urine colour and adjusting intake accordingly to stay within healthy ranges.
- Utilise electrolyte-rich beverages if engaging in prolonged or high-intensity workouts to replenish lost nutrients.
Post-exercise, rehydration is equally significant. Consuming fluids immediately after exercise assists in restoring lost fluids and supporting recovery. Aim for approximately 1.5 litres of water for every kilogram of body weight lost during exercise. Additionally, combining water intake with a small snack containing carbohydrates and protein can further enhance recovery.
Effective Hydration Strategies During Physical Activity
During exercise, particularly in hot climates, it is essential to drink water regularly to replace fluids lost through sweat. This practice helps maintain optimal hydration levels and supports sustained physical performance throughout the activity.
The best strategy involves sipping water frequently rather than consuming large quantities at once. Aim for:
- Small sips every 15-20 minutes during exercise to maintain optimal hydration levels.
- Monitor sweat rates: Individuals who sweat heavily may need to increase fluid intake accordingly to maintain hydration.
- Consider electrolyte replenishment: For workouts lasting over 60 minutes, especially in heat, integrate sports drinks or electrolyte tablets to enhance recovery.
- Listen to your body: Thirst is an indicator, but don’t wait until you’re thirsty; drink regularly throughout the activity to stay ahead of dehydration.
Implementing these strategies not only enhances performance but also ensures safety during workouts in hot climates, preventing heat-related illnesses and other complications.
Research-Backed Health Benefits of Staying Hydrated in Hot Climates
Key Health Benefits of Sustaining Hydration Levels
Maintaining proper hydration offers numerous health benefits, particularly in hot environments. Adequate fluid intake enhances cognitive function, mood, and physical performance, contributing to overall wellness. Hydration supports essential bodily processes and mitigates the risk of various health conditions associated with dehydration.
Studies have demonstrated that remaining well-hydrated can:
- Enhance cognitive function: Hydration is crucial for sustaining concentration and mental clarity, vital for productivity and learning.
- Improve mood: Proper hydration can prevent irritability and fatigue, positively impacting emotional well-being and enhancing quality of life.
- Support physical performance: Hydration is essential for maintaining endurance and strength during exercise, allowing individuals to reach their fitness goals.
- Prevent kidney stones and urinary tract infections: Increased fluid intake dilutes urine, lowering the likelihood of these painful conditions, which are more common in dehydrated individuals.
Encouraging a culture of hydration can lead to improved health outcomes, especially in hot environments where the risk of dehydration is markedly heightened.
Hydration’s Role in Promoting Skin Health
Adequate hydration plays a vital role in maintaining skin health and appearance. When the body is well-hydrated, skin elasticity improves, resulting in a more youthful and vibrant look. Proper hydration also helps prevent dryness, flakiness, and the formation of fine lines and wrinkles, contributing to an overall healthier appearance.
Several factors underline the connection between hydration and skin health:
- Enhanced elasticity: Hydration provides the necessary moisture to skin cells, promoting firmness and resilience against aging.
- Reduced dryness: Sufficient water intake keeps skin hydrated, lowering the risk of dryness and irritation.
- Toxin elimination: Drinking water helps the body flush out toxins, contributing to clearer skin and a healthier complexion.
- Prevention of acne: Proper hydration can help regulate oil production, reducing the likelihood of breakouts and promoting a clearer complexion.
Incorporating hydration into daily routines not only benefits overall health but also significantly enhances skin vitality, making it an essential aspect of beauty and wellness.
The Long-Term Benefits of Consistent Hydration
Consistent hydration contributes to long-term health benefits, including improved digestion, cardiovascular health, and overall physical well-being. Chronic dehydration can lead to numerous health complications, while maintaining optimal fluid levels promotes essential bodily functions, supporting longevity and vitality.
Key long-term effects of proper hydration include:
- Enhanced digestion: Adequate water intake supports digestive processes, promotes regular bowel movements, and prevents constipation.
- Improved cardiovascular health: Hydration helps maintain optimal blood volume and pressure, supporting overall heart function and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Weight management: Staying hydrated can help control appetite, making it easier to manage weight and support weight loss efforts.
- Improved kidney function: Consistent hydration helps prevent kidney stones and promotes efficient waste elimination, supporting overall kidney health.
Integrating hydration as a regular practice can lead to significant health improvements, ensuring individuals maintain their well-being over the long term and enjoy a high quality of life.
How Proper Hydration Prevents Heat-Related Illnesses
Effective hydration is critical in preventing heat-related illnesses, such as heat exhaustion and heatstroke, especially in hot climates. When the body becomes dehydrated, its ability to regulate temperature diminishes, significantly increasing the risk of overheating and associated health hazards.
Key strategies for preventing heat-related illnesses include:
- Consistent fluid intake: Ensure regular hydration before, during, and after exposure to high temperatures to maintain optimal fluid levels.
- Avoid peak heat hours: Schedule outdoor activities for the cooler parts of the day to minimise heat exposure and reduce dehydration risks.
- Recognise symptoms: Be aware of early signs of dehydration and heat stress, such as excessive sweating, dizziness, or confusion, enabling timely action.
- Implement cooling strategies: Use fans, cool showers, or wet towels to assist in temperature regulation and prevent overheating.
By prioritising hydration and understanding the risks associated with heat exposure, individuals can significantly reduce their chances of experiencing heat-related health issues and maintain their well-being.
The Role of Hydration in Enhancing Athletic Performance in Hot Conditions
Proper hydration is essential for boosting athletic performance, particularly in hot weather conditions. Sufficient fluid intake aids in maintaining blood volume, supporting muscle function, and promoting efficient thermoregulation during exercise, all crucial for optimal performance.
Key aspects of hydration’s impact on athletic performance encompass:
- Increased endurance: Hydration enables athletes to sustain performance levels longer, delaying fatigue and enhancing overall performance.
- Improved strength: Proper fluid balance supports muscle contraction and function, enhancing overall strength output and athletic capability.
- Faster recovery: Post-exercise hydration aids in muscle repair and replenishing glycogen stores, essential for recovery after rigorous activities.
- Optimised cardiovascular function: Dehydration can lead to elevated heart rates and reduced oxygen delivery to muscles, impairing performance and increasing fatigue.
Incorporating effective hydration strategies into training regimens is essential for athletes competing in hot environments, ensuring they can perform at their best while minimising health risks associated with dehydration.
Tailored Hydration Strategies for Different Age Groups
Understanding Hydration Needs for Children
Children are particularly vulnerable to dehydration due to their smaller body size and higher metabolic rates. Their unique physiology necessitates regular fluid intake, especially during physical activities or in hot conditions, to support their growth and development.
To encourage proper hydration in children, consider the following strategies:
- Establish a hydration routine: Make drinking water a regular part of their daily schedule, such as during meals, snacks, and breaks, to instil healthy habits.
- Monitor activity levels: Ensure children drink water before, during, and after engaging in physical activities to prevent dehydration.
- Utilise appealing containers: Fun and colourful water bottles can motivate children to consume more fluids and make hydration enjoyable.
- Incorporate hydrating foods: Offer fruits and vegetables with high water content, such as watermelon and cucumbers, to further contribute to overall hydration.
By fostering a culture of hydration among children, caregivers can help instil lifelong healthy habits that support their growth and development, ensuring they stay active and healthy.
Promoting Hydration for the Elderly Population
Older adults may experience a diminished sense of thirst, increasing their risk of dehydration. Additionally, age-related physiological changes can impact fluid balance and kidney function, necessitating a focused approach to hydration in this demographic.
To enhance hydration among older individuals, consider these strategies:
- Encourage regular water intake: Remind older adults to drink water throughout the day, even if they don’t feel thirsty, to maintain adequate hydration levels.
- Monitor medications: Be aware of medications that can impact hydration, such as diuretics, and adjust fluid intake accordingly to avoid dehydration.
- Offer flavoured water: Adding natural flavours like lemon or cucumber can make water more enjoyable and encourage older adults to drink more.
- Provide accessible options: Ensure water is readily available by placing bottles or pitchers near seating areas to encourage frequent sipping.
By being proactive about hydration needs, caregivers can help older adults maintain their health and prevent dehydration-related complications, enhancing their quality of life.
Specific Hydration Strategies for Athletes
Athletes have heightened hydration needs due to increased physical activity and significant sweat loss during training and competition. Developing a comprehensive hydration plan is essential for optimising performance and recovery in this population.
Key hydration tips for athletes include:
- Pre-hydrate adequately: Aim to drink 16-20 ounces of water 2 hours before exercising to ensure proper fluid levels are established.
- Drink regularly during exercise: Consume 7-10 ounces of fluid every 10-20 minutes during workouts to replace lost fluids effectively.
- Incorporate electrolytes: Use electrolyte-rich beverages if exercising for over an hour or in extreme heat to replenish lost electrolytes and maintain performance.
- Rehydrate post-exercise: Drink 1.5 litres of fluid for every kilogram of body weight lost during activity to support recovery and fluid balance restoration.
Implementing these hydration strategies can significantly enhance athletic performance and support recovery, particularly in challenging weather conditions, allowing athletes to perform at their best.
Hydration Recommendations for Pregnant Women
Pregnant women experience increased fluid requirements to support blood volume expansion and fetal development. Staying well-hydrated is essential for both maternal and fetal health, promoting optimal growth and development.
To ensure proper hydration, pregnant women should consider:
- Aim for 8-12 cups of water daily, adjusting intake based on activity levels and environmental conditions to meet their fluid needs.
- Incorporate hydrating foods: Consume fruits and vegetables that are high in water content to boost fluid intake and support overall hydration.
- Monitor symptoms: Be attentive to signs of dehydration, such as dry skin or fatigue, and increase fluid intake as necessary to prevent complications.
- Stay aware of activity levels: Ensure hydration is prioritised during physical activities or hot weather conditions to support both maternal and fetal health.
By focusing on hydration, pregnant women can support their own health as well as that of their developing child, ensuring a healthy pregnancy.
Hydration Tips for Working Professionals
Working adults often overlook hydration due to busy schedules and long hours at their desks. Maintaining adequate hydration levels is crucial for productivity, cognitive function, and overall well-being in the workplace.
To promote hydration among professionals, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Keep a water bottle at your desk: Having water readily accessible encourages regular sipping and can serve as a visual reminder to drink.
- Set reminders: Utilise phone alarms or hydration apps to remind you to drink water throughout the day, preventing dehydration.
- Incorporate hydration breaks: Schedule short breaks during meetings or tasks to refill and drink water, which can also improve focus and productivity.
- Choose hydrating snacks: Opt for fruits and vegetables as snacks to contribute to overall fluid intake and enhance hydration.
By integrating these practical tips into their daily routines, working professionals can ensure they remain adequately hydrated, enhancing their performance and well-being at work.
The Interplay Between Hydration and Diet
Recognising the Most Hydrating Foods and Beverages
Foods and beverages play a significant role in maintaining hydration levels, especially in hot climates. Consuming items with high water content can effectively complement fluid intake and provide hydration through diet.
Examples of hydrating foods and beverages include:
- Watermelon: Comprising approximately 92% water, it serves as a delicious and effective way to boost hydration levels.
- Cucumbers: With a water content of around 95%, they are ideal for snacking and adding to salads to enhance hydration.
- Oranges: These juicy fruits provide hydration along with essential vitamins and minerals, supporting overall health.
- Coconut water: A natural source of electrolytes, it can replenish fluids lost through sweating while providing added nutrients.
Incorporating these hydrating options into daily meals and snacks can significantly enhance overall fluid intake, particularly in hot weather, ensuring optimal hydration.
Understanding the Impact of Diet on Hydration Levels
Diet plays a critical role in hydration levels, as the types of foods consumed can either support or hinder fluid balance. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables generally aids in maintaining adequate hydration, while excessive sodium intake may lead to increased fluid loss and dehydration.
Consider the following dietary impacts on hydration:
- High sodium diets: Consuming too much salt can deplete hydration levels, leading to increased thirst, fluid retention, and potential health issues.
- Fruits and vegetables: A diet high in these foods contributes significantly to hydration due to their high water content and nutrient density.
- Balanced electrolyte intake: Ensuring adequate consumption of potassium-rich foods helps maintain fluid balance and supports overall hydration.
- Moderation of caffeine: While moderate caffeine consumption is acceptable, excessive intake can contribute to dehydration and adversely affect hydration status.
Understanding the relationship between diet and hydration empowers individuals to make informed dietary choices that effectively support their hydration needs and overall health.
Strategies to Avoid Dehydrating Substances
Certain substances can act as diuretics, leading to increased urine production and potential dehydration. Caffeine and alcohol, in particular, should be consumed in moderation, especially in hot climates where hydration is critical for health and safety.
Key considerations for avoiding dehydrating substances include:
- Moderation of caffeine: Limit intake to avoid excessive fluid loss, especially before and during physical activity to maintain hydration.
- Responsible alcohol consumption: Drink responsibly and ensure to balance alcoholic beverages with adequate water intake to prevent dehydration.
- Hydration strategies: Pair caffeinated or alcoholic beverages with water to mitigate dehydration effects and maintain fluid balance.
- Awareness of personal tolerance: Understand how your body reacts to these substances to adjust intake accordingly and avoid dehydration.
By being mindful of these dehydrating substances and implementing moderation, individuals can effectively support their hydration efforts and maintain overall health.
Common Questions About Hydration Answered
What is the recommended water intake during exercise in hot weather?
During physical activity in hot weather, it’s advisable to drink 7-10 ounces every 10-20 minutes. Adjust your intake based on sweat loss and exercise intensity to maintain optimal hydration levels.
What are the common signs of dehydration?
Signs of dehydration include thirst, dry mouth, dizziness, fatigue, and decreased urine output. Monitoring these symptoms can help prevent severe dehydration and associated health complications.
Are sports drinks necessary during workouts?
Sports drinks can be beneficial for prolonged or intense workouts, especially in heat. However, for shorter activities, water is often sufficient for maintaining hydration and performance.
How can I encourage children to stay hydrated?
Encourage hydration by scheduling regular water breaks, serving hydrating foods, and using fun drink containers to make water more appealing and enjoyable for children.
What role do electrolytes play in hydration?
Electrolytes are essential for maintaining fluid balance in the body. They are lost through sweat and should be replenished during prolonged physical activity to support optimal hydration and bodily functions.
Is it possible to stay hydrated without drinking water?
Yes, you can maintain hydration by consuming hydrating foods (e.g., fruits and vegetables) and beverages like herbal teas and coconut water, which contribute to your overall fluid intake and hydration levels.
What are the risks of dehydration in hot climates?
Dehydration in hot climates can lead to heat exhaustion, heatstroke, decreased cognitive function, and impaired physical performance, making hydration crucial for health and safety in such environments.
How can I assess if I’m drinking enough water?
You can evaluate hydration by checking the colour of your urine; pale yellow indicates proper hydration, while dark yellow suggests dehydration and the need for increased fluid intake.
Do athletes have specific hydration tips?
Athletes should pre-hydrate, drink regularly during activity, and incorporate electrolyte-rich beverages for prolonged or intense workouts to support optimal hydration and performance.
How does age impact hydration needs?
Children and older individuals often have different hydration needs. Children require regular fluids due to their smaller size, while older adults may not feel thirsty and often need reminders to drink water consistently.
Connect with us on Facebook!
The Article Hydration for Hot Climates: Essential Tips appeared first on https://athleticsupplement.com
The Article Hydration Tips for Staying Cool in Hot Climates Was Found On https://limitsofstrategy.com
References:
https://limitsofstrategy.com/hydration-tips-for-staying-cool-in-hot-climates-2/